Here is the note for Salesforce Basics tutorial on Trailhead.
Get Started with the Salesforce Platform
What does Salesforce Platform offer?
- Develop custom data models and applications for desktop and mobile.
- Heroku platform which let developers build scalable web apps and backend services by several languages.
- Salesforce APIs, which let developers integrate and connect their enterprise data.
- Mobile SDK.
- so on
Develop without code
What is metadata
In short, metadata forms structure of your organization.
Code with Salesforce Languages
There are three core programmatic technologies to learn about as a Salesforce developer.
- Lightning Component Framework: A UI development framework similar to AngularJS or React.
- Apex: Salesforce’s proprietary programming language with Java-like syntax.
- Visualforce: A markup language that lets you create custom Salesforce pages with code that looks a lot like HTML, and optionally can use a powerful combination of Apex and JavaScript.
The difference between Lightning components and Visualforce pages.:
- The primary difference is right in the name. With Lightning components, you’re developing components that can be pieced together to create pages. With Visualforce, you’re developing entire pages at once.
- While Lightning components are newer and better for things like mobile development, there are several situations where it can make more sense to use Visualforce.
Extend the Salesforce Platform
Get to Know the Lightning Platform APIs
The __c denotes that the object is a custom object or field. This query is using the automatically created API access point for the Property object to retrieve information about properties in your org.
Unleash Your Apps with Heroku
Heroku is a web development platform that lets you quickly build, deploy, and scale web apps.
Import Data
Introduction to Data Import
Salesforce offers two main methods for importing data.
- Data Import Wizard—this tool, accessible through the Setup menu, lets you import data in common standard objects, such as contacts, leads, accounts, as well as data in custom objects. It can import up to 50,000 records at a time. It provides a simple interface to specify the configuration parameters, data sources, and the field mappings that map the field names in your import file with the field names in Salesforce.
- Data Loader—this is a client application that can import up to five million records at a time, of any data type, either from files or a database connection. It can be operated either through the user interface or the command line. In the latter case, you need to specify data sources, field mappings, and other parameters via configuration files. This makes it possible to automate the import process, using API calls.
Here are different situations for different tools:
Use the Data Import Wizard When:
- You need to load less than 50,000 records.
- The objects you need to import are supported by the wizard.
- You don’t need the import process to be automated.
Use Data Loader When:
- You need to load 50,000 to five million records. If you need to load more than 5 million records, we recommend you work with a Salesforce partner or visit the AppExchange for a suitable partner product.
- You need to load into an object that is not supported by the Data Import Wizard.
- You want to schedule regular data loads, such as nightly imports.
Add Field Access with a Permission Set
Remember, a permission set is for expanding a user’s access to fields that are restricted in their profile.
Use Formula Fields
The Formula Editor in Action
Example 1: Displaying an Account Field on the Contact Detail Page
Example 2: Displaying the Number of Days Until an Opportunity Closes on a Report
In this part, the most important part is to use TODAY to get the value of today.
Example 3: Finding Distinct Objects Using the Power of One
It is used to figure out the number of distinct items, such as there are only 6 users but 100 records related, Power of One can do the distinction.
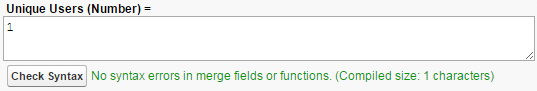
To write this formula, create a custom formula field on the User object. Name it Unique Users, give it a Number return type, and select 0 from the Decimal Places drop-down list. Click Next to open the formula editor. For this formula, you don’t need to insert any fields, operators, or functions. Instead, enter the number 1.
Yes,just the number 1.
Debugging Formulas
So we can also check the formula online. Such as :
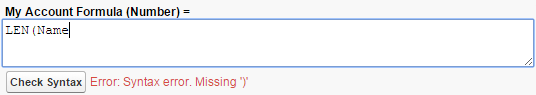
- Missing parentheses: This error most often occurs when the number of opening parentheses doesn’t match the number of closing parentheses. It can be particularly difficult to avoid this error if you’re using several functions at once. Try breaking your function into multiple lines so it’s easier to tell which sets of parentheses belong together.
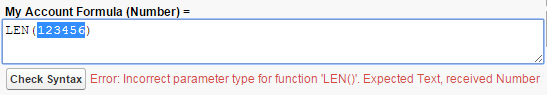
- Incorrect parameter type: If you give a function a number parameter when it expects text (or any other combination of data types), this is the error you’ll see. Always check the help text or the documentation so you know what kind of parameters a function accepts.
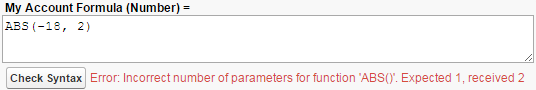
- Incorrect number of parameters for function: If you input too many or too few parameters into a function, the syntax checker alerts you. Again, check the help text or documentation for guidelines on inputting parameters to specific functions.
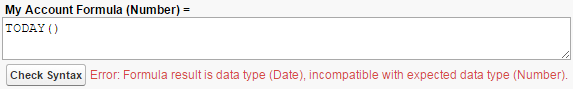
- Formula result is incompatible with formula return type: You’ll see this error if you select one data type when creating the formula field but write a formula that returns a different data type. In the example below, you can see that My Account Formula expects to return a number (shown in parentheses next to the formula name), but the TODAY() function returns a date. The error tells you what the expected data type is, but you can always reference the documentation beforehand to avoid the error.
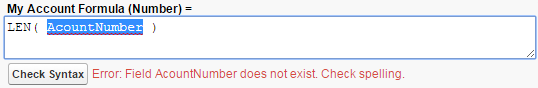
- Field does not exist: This error indicates that you’ve included a field in your formula that your object doesn’t support. In this case, check your spelling and capitalization. If you can’t find any mistakes, try inserting the field from the Insert Field menu again to make sure you’re referencing it correctly.
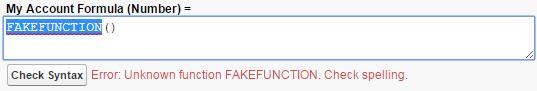
- Unknown function: In this case, check that Salesforce supports the functions you’re using. You’ll also get this error for misspelled functions.
Implement Roll-Up Summary Fields
This part is used for the Master-Detail relationship for the records.
Keep in mind that the types of fields you can calculate in a roll-up summary field depend on the type of calculation. For example:
- Number, currency, and percent fields are available when you select SUM as the roll-up type.
- Number, currency, percent, date, and date/time fields are available when you select MIN or MAX as the roll-up type.
Create Validation Rules
Just create validation by clicking.
Here are some examples:
Account Number Is Numeric
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Description: | Validates that the Account Number is numeric if not blank. |
| Formula: | ` AND( NOT(ISBLANK(AccountNumber)), NOT(ISNUMBER(AccountNumber)) )` |
| Error Message: | Account Number is not numeric. |
| Error Location: | Account Number |
Date Must Be in the Current Year
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Description: | Validates that a custom date field contains a date within the current year. |
| Formula: | YEAR( My_Date__c ) <> YEAR ( TODAY() ) |
| Error Message: | Date must be in the current year. |
| Error Location: | My Date |
Number Range Validation
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Description: | Validates that the range between two custom fields, Salary Min and Salary Max, is no greater than $20,000. |
| Formula: | (Salary_Max__c - Salary_Min__c) > 20000 |
| Error Message: | Salary range must be within $20,000. Adjust the Salary Max or Salary Min values. |
| Error Location: | Salary Max |
Website Extension
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Description: | Validates a custom field called Web Site to ensure that its last four characters are in an explicit set of valid website extensions. |
| Formula: | OR( RIGHT( Web_Site__c, 4) <> ".COM", RIGHT( Web_Site__c, 4) <> ".com", RIGHT( Web_Site__c, 4) <> ".ORG", RIGHT( Web_Site__c, 4) <> ".org", RIGHT( Web_Site__c, 4) <> ".NET", RIGHT( Web_Site__c, 4) <> ".net" ) |
| Error Message: | Web Site must have an extension of .com, .org, or .net. |
| Error Location: | Web Site |
Valid Billing Country
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Description: | Validates that the account Billing Country is a valid ISO 3166 two-letter code. |
| Formula: | OR( LEN(BillingCountry) = 1, NOT( CONTAINS( "AF:AX:AL:DZ:AS:AD:AO:AI:AQ:AG:AR:AM:" & "AW:AU:AZ:BS:BH:BD:BB:BY:BE:BZ:BJ:BM:BT:BO:" & "BA:BW:BV:BR:IO:BN:BG:BF:BI:KH:CM:CA:CV:KY:" & "CF:TD:CL:CN:CX:CC:CO:KM:CG:CD:CK:CR:CI:HR:" & "CU:CY:CZ:DK:DJ:DM:DO:EC:EG:SV:GQ:ER:EE:ET:FK:" & "FO:FJ:FI:FR:GF:PF:TF:GA:GM:GE:DE:GH:GI:GR:GL:" & "GD:GP:GU:GT:GG:GN:GW:GY:HT:HM:VA:HN:HK:HU:" & "IS:IN:ID:IR:IQ:IE:IM:IL:IT:JM:JP:JE:JO:KZ:KE:KI:" & "KP:KR:KW:KG:LA:LV:LB:LS:LR:LY:LI:LT:LU:MO:MK:" & "MG:MW:MY:MV:ML:MT:MH:MQ:MR:MU:YT:MX:FM:MD:MC:" & "MC:MN:ME:MS:MA:MZ:MM:MA:NR:NP:NL:AN:NC:NZ:NI:" & "NE:NG:NU:NF:MP:NO:OM:PK:PW:PS:PA:PG:PY:PE:PH:" & "PN:PL:PT:PR:QA:RE:RO:RU:RW:SH:KN:LC:PM:VC:WS:" & "SM:ST:SA:SN:RS:SC:SL:SG:SK:SI:SB:SO:ZA:GS:ES:" & "LK:SD:SR:SJ:SZ:SE:CH:SY:TW:TJ:TZ:TH:TL:TG:TK:" & "TO:TT:TN:TR:TM:TC:TV:UG:UA:AE:GB:US:UM:UY:UZ:" & "VU:VE:VN:VG:VI:WF:EH:YE:ZM:ZW", BillingCountry))) |
| Error Message: | A valid two-letter country code is required. |
| Error Location: | Billing Country |
Automate Simple Business Processes with Process Builder
The Components of a Process
Every process consists of a trigger, at least one criteria node, and at least one action. You can configure immediate actions or schedule actions to be executed at a specific time.
There are 2 kinds of actions that the Process can do:
- Each immediate action is executed as soon as the criteria evaluates to true.
- Each scheduled action is executed at the specified time, such as 10 days before the record’s close date or 2 days from now. At the specified time, Salesforce makes sure that the associated criteria node still evaluates to true. If so, the scheduled action is executed.